| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
Tags
- 딥러닝
- ue5.4
- 오블완
- deep learning
- Generative Model
- Diffusion
- 모션매칭
- GAN
- userwidget
- motion matching
- BERT
- 폰트생성
- NLP
- Few-shot generation
- Stat110
- 언리얼엔진
- WBP
- RNN
- UE5
- dl
- CNN
- multimodal
- animation retargeting
- Font Generation
- 디퓨전모델
- 생성모델
- WinAPI
- cv
- Unreal Engine
- ddpm
Archives
- Today
- Total
Deeper Learning
[Statistics 110] Lecture 29: Law of Large Numbers and Central Limit Theorem 본문
Statistics & Math/Statistics 110: Probability
[Statistics 110] Lecture 29: Law of Large Numbers and Central Limit Theorem
Dlaiml 2023. 1. 28. 16:09Law of Large Numbers(큰 수의 법칙)
X1,...,Xn이 i.i.d 이며 평균 μ, 표준편차 σ2일 때, 표본평균 ˉXn=1n∑nj=1Xj라고 정의
Strong LLN: n이 무한으로 가면 1의 확률로 ˉXN 이 μ로 간다. (표본평균이 모평균에 근사)
Weak LLN: 모든 c>0에 대해 n이 무한으로 가면, P(|ˉXn−μ|>c)→0.
체비셰프 부등식을 활용한 Weak LLN 증명

ˉXn−μ가 0으로 수렴한다는 것은 알지만, ˉXn 분포에 대한 정보는 아직 알 수 없음
무한으로 가는 무언가와 곱하여 힌트를 얻을 수 있음 (n3을 곱하였을 때 무한이 되거나 0이 되는것을 관찰하고 얼마나 빠른 속도로 ˉXn이 μ에 수렴하고 있는지 확인)
Central Limit Theorem(중심극한정리)

Normal Approximation to Binomial
X∼Bin(n,p), X=∑nj=1Xj,Xj∼Bern(p) i.i.d.
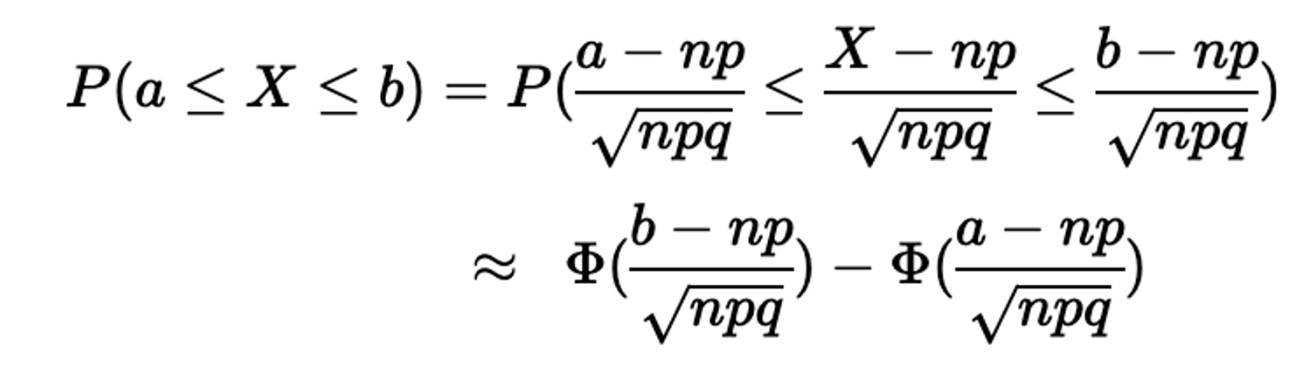
p가 1/2에 가깝고 n이 클 때 정규분포로의 근사가 빠르게 이루어짐 (포아송분포로의 근사는 p가 작을 때 용이)
Reference
[0] https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL2SOU6wwxB0uwwH80KTQ6ht66KWxbzTIo
'Statistics & Math > Statistics 110: Probability' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Statistics 110] Lecture 31: Markov Chains (0) | 2023.01.28 |
|---|---|
| [Statistics 110] Lecture 30: Chi-Square, Student-t, Multivariate Normal (0) | 2023.01.28 |
| [Statistics 110] Lecture 28: Inequalities (0) | 2023.01.28 |
| [Statistics 110] Lecture 27: Conditional Expectation given an R.V. (0) | 2023.01.28 |
| [Statistics 110] Lecture 25: Order Statistics and Conditional Expectations (0) | 2023.01.28 |
Comments